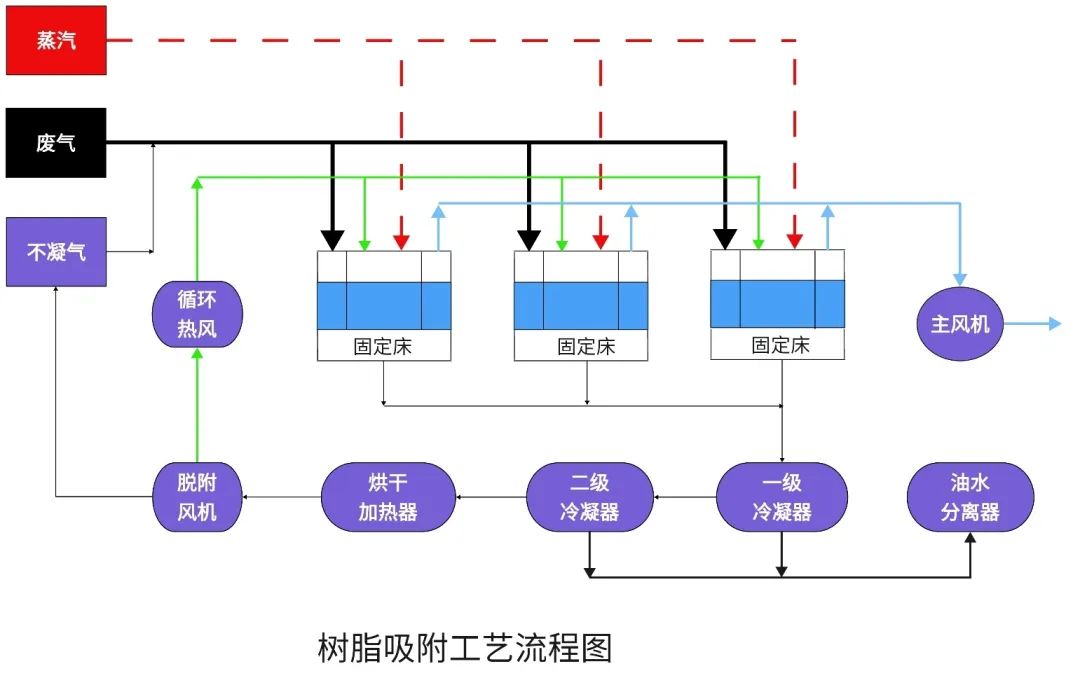
Resin adsorption desorption
Overview: Resin adsorption desorption+condensation recovery technology is a VOCs organic waste gas treatment technology that combines adsorption and condensation methods. This technology fully utilizes the advantages of both methods and has the characteristics of high purification efficiency, stable treatment indicators, low resin loss, long service life, high efficiency and low loss. The treatment cost is lower than that of activated carbon adsorption recovery technology.
Requirements for resin adsorption technology
1、Basic requirements:
1.1 Resin adsorption treatment technology is suitable for treating medium and low air volume organic waste gas, where the boiling point of organic matter should be less than 150 ℃ and it should be liquid at room temperature.
1.2 The exhaust gas flow rate entering the adsorption device should be less than 10000m³/h;
The temperature of the exhaust gas entering the adsorption device should be below 40 ℃.
The particle content entering the adsorption device should be less than 1mg/m³.
At present, the production technology of adsorption resin in China has also been improved to some extent, but the products of different manufacturers and models vary greatly, with significant differences in performance. The BET specific surface area of the adsorption resin should not be less than 1000m2/g, the micropore volume should not be less than 0.4ml/g, and the total pore volume should not be less than 0.9ml/g; The particle size between 0.45-1.25mm is greater than 95%; The spherical rate after grinding is greater than 95%; The moisture content is 50-60%; Wet density 0.68-0.7g/ml; PH value is 7.0-7.5.
2、Process design requirements
2.1 Preprocessing
Due to the vastly different properties of exhaust gases generated in various industries, and the strict requirements of adsorption methods for dust, aerosols, and substances that can cause adsorbent poisoning in exhaust gases, the pre-treatment system of exhaust gases has a huge impact on adsorption equipment.
In industrial organic waste gas, there is usually a small amount of dust, but in some process waste gases, the dust content can be very high, and in spraying waste gases, there is a large amount of paint mist. Particles and other substances usually exist in the form of aerosols. The adsorption system is highly sensitive to dust, paint mist, and aerosols, which can seriously affect the stable operation of the adsorption system. Therefore, before the exhaust gas enters the adsorber, the dust and paint mist must be cleaned up, and the aerosols must be destroyed. At present, in some adsorption purification equipment in China, due to insufficient attention to the pre-treatment of exhaust gas or improper use of pre-treatment equipment, the efficiency of adsorbers is very low, and some cannot be used for a long time.
The exhaust gas pretreatment process mainly includes two processes: mechanical filtration and wet spray absorption, and a combination of dry and wet processes can also be used.
In the mixed waste gas generated by many processes such as spraying, pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and chemical fiber production, there are often some high boiling point macromolecular compounds, such as dimethyl pentanone (boiling point 164 ° C) in electrical spraying waste gas, which are difficult to desorb after being adsorbed by the adsorption resin and cause resin poisoning. Although these substances are not high in content, they are difficult to desorb after adsorption and accumulate in the adsorbent, causing the adsorption resin to quickly become toxic and ineffective. High boiling point macromolecular organic compounds are removed before production through enhanced condensation or pre adsorption devices using activated carbon/resin.
The pressure loss of a general pre-treatment device will not exceed 1kPa, but when using a bag filter for filtration, the pressure loss will exceed 1kPa.
2.2 Adsorption
In HJ/T386-2007 "Industrial Waste Gas Adsorption Purification Equipment", principle requirements are made for the basic performance of adsorption devices.
The airflow velocity of the adsorption layer is the main parameter in the design of fixed bed adsorbers. Due to the significant differences in adsorption capacity, adsorption rate, and adsorption layer resistance among different types of adsorbents, the airflow velocity should be selected based on a combination of adsorption rate and adsorption layer resistance. The particle size of adsorption resin particles is generally 0.4-1.2mm. When the bed resistance is less than 2kPa, the airflow speed should generally be between 015-0.25m/s.
The dosage of adsorbent should be determined based on the dynamic adsorption capacity of the adsorption bed during one adsorption cycle. The dynamic adsorption capacity is determined by the saturated adsorption capacity, adsorption rate, temperature, pressure, and concentration of organic matter of the adsorbent, and should generally be determined based on experiments. After determining the adsorption period and dynamic adsorption capacity of the adsorbent, the amount of adsorbent used is often calculated using the Schieloef formula or other empirical calculation methods.
The pressure loss of the adsorber should be less than 4.5kPa. According to HJ/T386-2007 "Industrial Waste Gas Adsorption Purification Device", the pressure loss of the adsorption device shall not exceed 2.5kPa. In practical applications, especially when using a 2-tower series adsorption process, the design resistance may sometimes exceed 2.5 kPa. According to the current practical application of the adsorption device, it is stipulated that the pressure loss of the adsorption device should be less than 4.5 kPa.
2.3 Adsorbent regeneration
When using steam replacement regeneration, low-pressure steam is generally used, which has a high temperature and high pressure resistance requirements for the equipment. Based on experience, it is generally considered that the temperature of water vapor should be below 140°C.
When adsorbents that adsorb organic compounds are regenerated by blowing with hot air flow, there are significant safety hazards. When using hot air flow to regenerate adsorbents, it is actually a non steady state process. If the temperature and air volume of the hot air flow entering the adsorber remain constant, due to the high concentration of organic matter in the adsorbent at the beginning, the concentration of organic matter in the exhaust gas of the adsorber may also be high, which may exceed the 25% concentration limit of its lower explosive limit, posing a risk of explosion. Therefore, the key is to strictly control the temperature of the hot gas flow entering the adsorber. The initial temperature can be lower, and as the regeneration process progresses, the temperature of the regeneration gas flow can be appropriately increased.
2.4 Safety Measures
(1) Due to the flammability and explosiveness of organic waste gas, safety measures are the first factor to be considered in the process design of organic waste gas treatment devices. In addition to complying with relevant regulations on safety production and accident prevention, automatic accident alarm devices must be installed in the process system.
(2) Reliable flame arresters should be installed at appropriate positions between the exhaust gas treatment system and the main production equipment, as well as in the pipeline system. The performance of flame arresters should be inspected in accordance with the provisions of 5.4 in HJ/T 389-2007. At least flame arresters should be installed between the organic waste gas treatment system and the main production equipment.
(3) Fans, motors, and electrical equipment placed on site should have explosion-proof functions. For the treatment of organic waste gas, explosion-proof fans, motors, and control cabinets must be selected.
(4) Due to the fact that the adsorption process is an exothermic process, when dealing with high concentration organic waste gas, if the heat dissipation effect of the adsorber is not good, there will be a significant temperature rise in the adsorber. An increase in temperature inside the adsorber not only reduces the adsorption efficiency of the adsorbent, but also poses a risk of fire and explosion. Therefore, fire and explosion prevention devices should be regularly installed. In fact, for the adsorption of generally low concentration organic waste gas, the temperature rise of the adsorption bed is often very low.
(5) When using inert gas hot gas blowing method for regeneration, according to experience, it is relatively safe to control the temperature of the hot gas flow below 150 ° C.
(6) For the depressurization desorption process, the highest explosion-proof level is required for the system fan, vacuum desorption pump, and electrical system, and intrinsically safe explosion-proof devices that meet the requirements of GB3836.4 should be used.